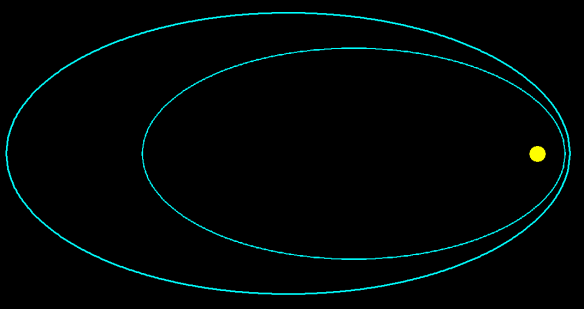
The picture above shows a proposed model for the production of a sudden increase in the brightness of a star — or rather, what is apparently a single star, optically, but would actually be a suddenly-produced binary stellar system.
The yellow object is a star, the system’s primary, and it has high mass (at least a few solar masses), when its mass is compared to those of the brown dwarfs in the two highly elliptical orbits shown in blue. These brown dwarfs aren’t quite stars, lacking enough mass to fuse hydrogen-1, which requires 75 to 80 Jupiter masses, but one of them (the larger one) is close to that limit. The smaller brown dwarf has perhaps half the mass of the larger brown dwarf. Their high orbital eccentricities give them very long orbital periods, on the order or 100,000 years. In a very small fraction of orbits, both brown dwarfs will be near perihelion (closest point to the primary) at the same time, and, during those rare periods, the two brown dwarfs become much closer to each other than they are to the primary.
When the two brown dwarfs become close enough to each other, matter from the smaller one could be drawn, by gravity, into the larger brown dwarf, increasing its mass, at the expense of its smaller sibling. At some point, in such a system, the larger brown dwarf’s mass could then reach the threshold to begin fusing hydrogen-1, and “turn on” as a true star — a red dwarf. From Earth, this red dwarf would not be distinguishable from the system’s most massive star, shown in yellow, until much later, when the two moved further apart. There would, however, be a sudden increase in luminosity from the system as a whole. Unlike other types of novae, this increase in luminosity would not fade away quickly, for red dwarfs have very long lifespans. This would enable them, upon discovery, to be distinguished from other single-brightening stellar events. Confirmation could then come from resolution of the new red dwarf component, as it recedes from the primary, making detection easier.
For a variation on this mechanism, the primary star could be somewhat more massive, and the two large brown dwarfs could be replaced by two large red dwarf stars. The larger red dwarf could draw matter from the smaller one, until the larger red dwarf became large enough to cross a higher mass threshold, and brighten substantially, with its color suddenly changing to orange or yellow.
A problem for this model: no such events are known to have happened. If they do happen, a likely explanation for their rarity is the likelihood that such orbits would be unstable, in a large fraction of similar cases, preventing the stellar-brightening event from having time to happen — in all but a few cases, none of which humans have (yet) both seen, and understood. If one of these things goes off nearby, though, we will learn about it quickly, for it will make itself known.
For another possible mechanism, there is another option: remove the primary altogether, and let the two objects of near-threshold mass orbit their common center of mass directly. They could then create a new star, or brighter star, by the mechanism described, one which might even produce a detectable accretion disk. A actual merger of the two brown dwarfs, or red dwarf stars, would be a variation of this idea, and would presumably be more likely if the two objects had masses very close to each other, so that neither would have an advantage in the gravitational tug-of-war.