These two polyhedra are the truncated tetrahedron on the left, plus at least one faceted version of that same Archimedean solid on the right. As you can see, in each case, the figures have the same set of vertices — but those vertices are connected in a different way in the two solids, giving the polyhedra different faces and edges.
(To see larger images of any picture in this post, simply click on it.)
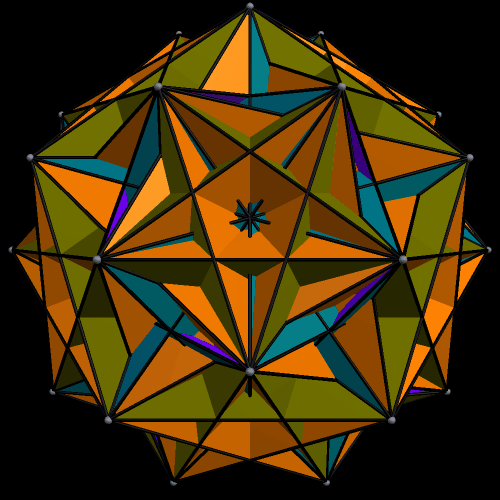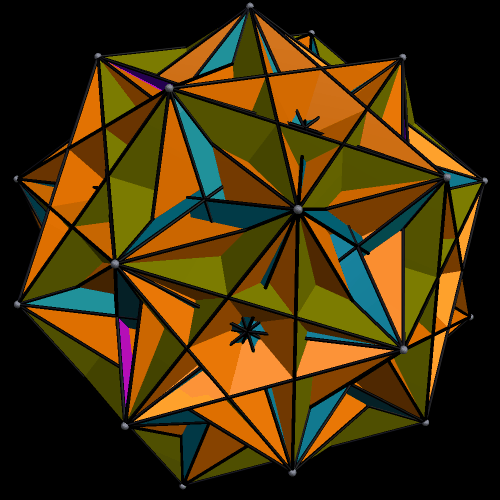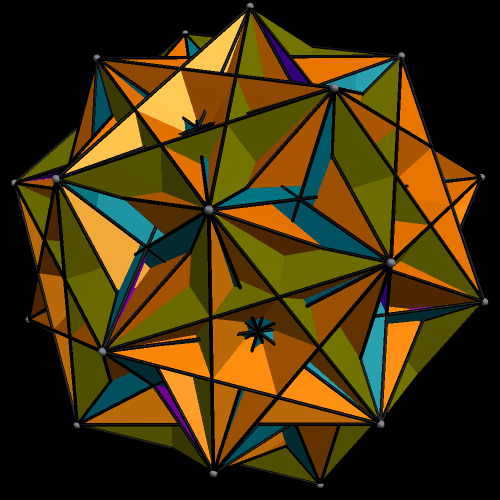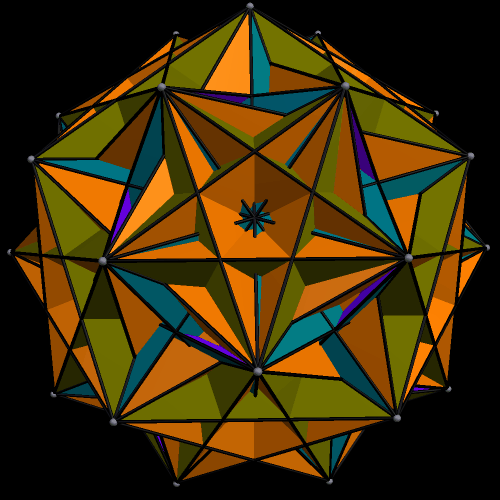
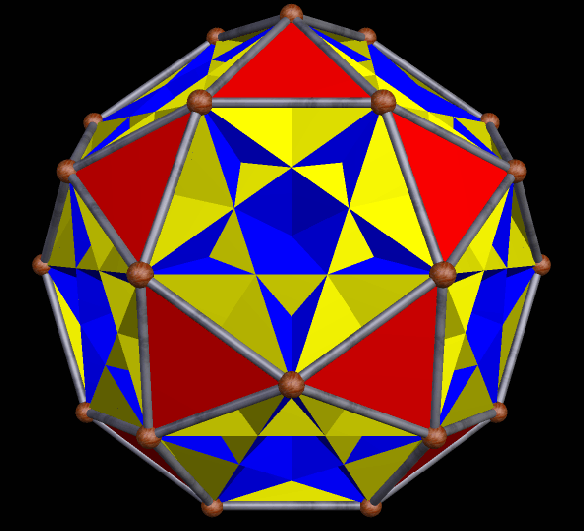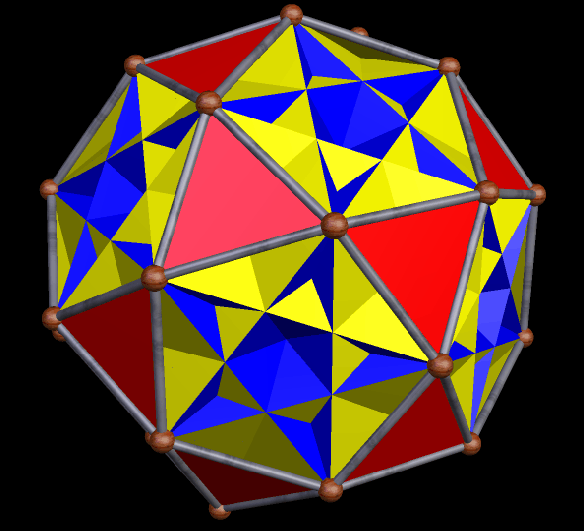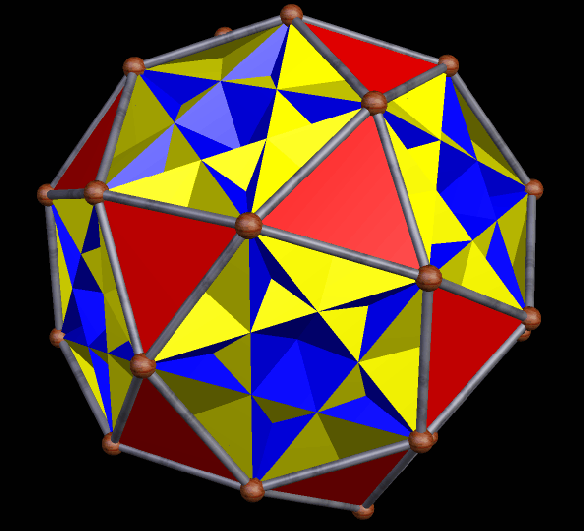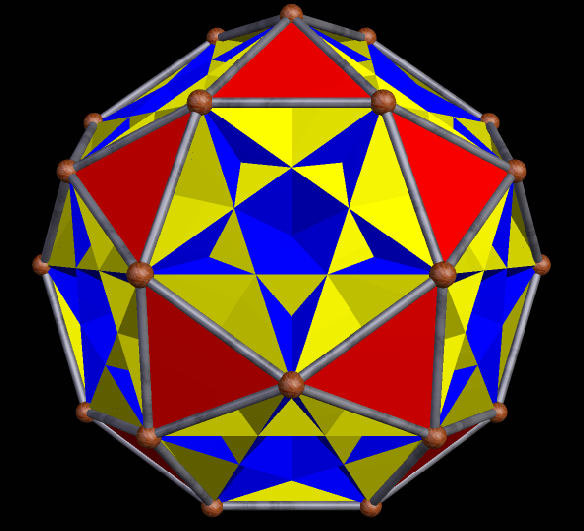
The next three are the truncated cube, along with two different faceted truncated cubes on the right. The one at the top right was the first one I made — and then, after noticing its chirality, I made the other one, which is the compound of the first faceted truncated cube, plus its mirror-image. Some facetings of non-chiral polyhedra are themselves non-chiral, but, as you can see, chiral facetings of non-chiral polyhedra are also possible.
The next two images show a truncated octahedron, along with a faceted truncated octahedron. As these images show, sometimes faceted polyhedra are also interesting polyhedra compounds, such as this compound of three cuboids.
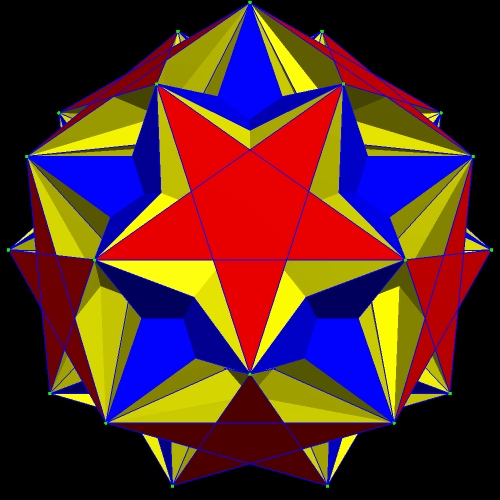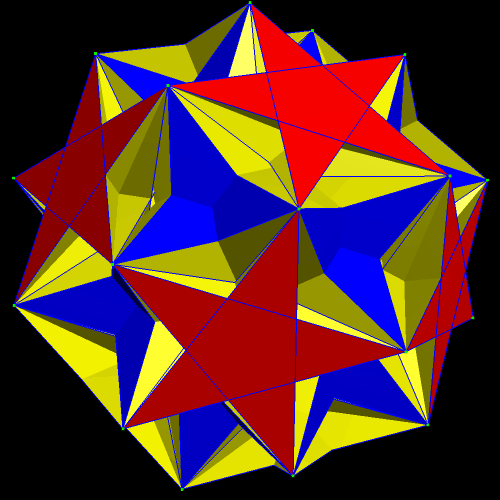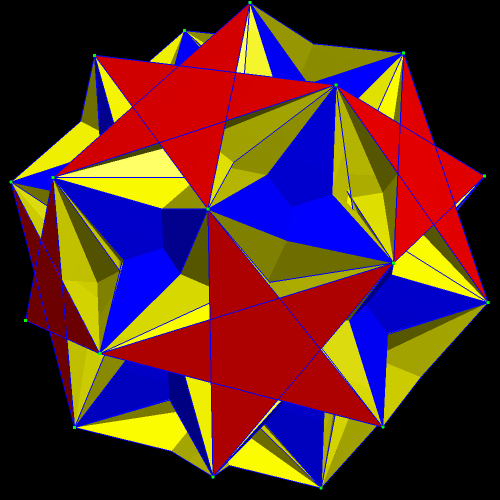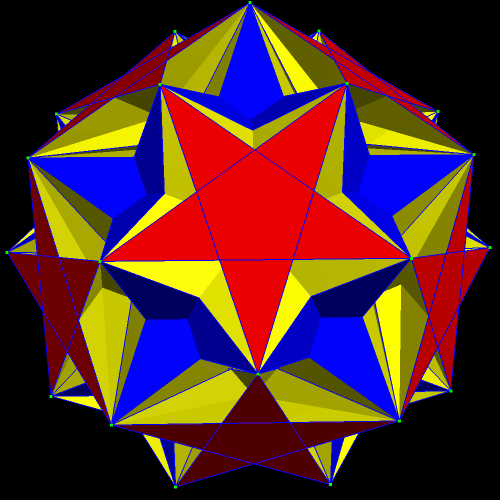
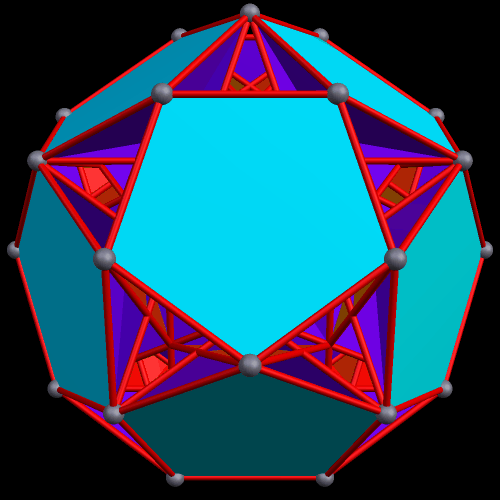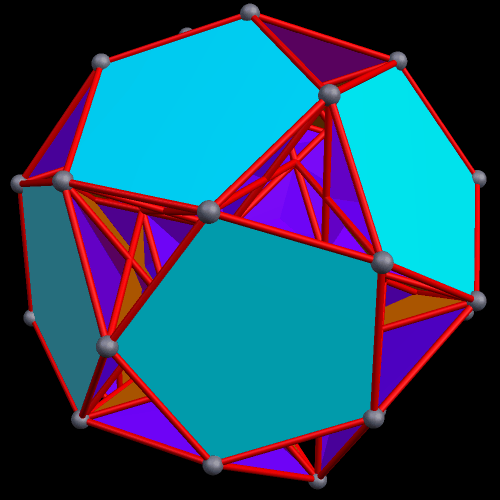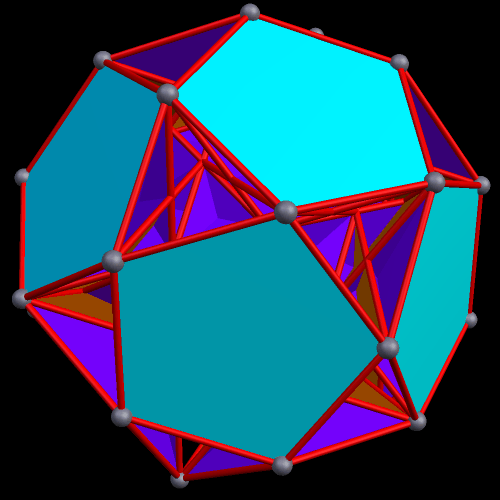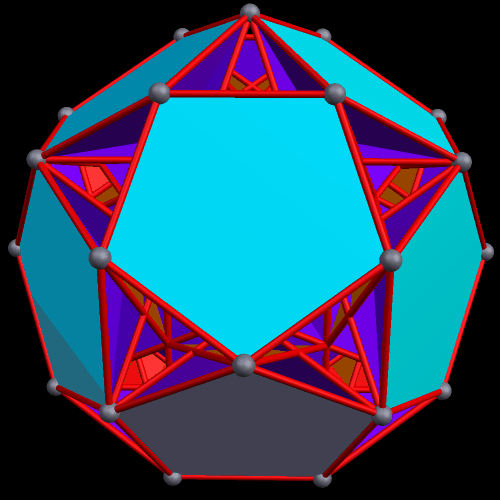
The next polyhedra shown are a truncated dodecahedron, and a faceted truncated dodecahedron. Although faceted polyhedra do not have to be absurdly complex, this pair demonstrates that they certainly can be.
Next are the truncated icosahedron, along with one of its many facetings — and with this one (below, on the right) considerably less complex than the faceted polyhedron shown immediately above.
The next two shown are the cuboctahedron, along with one of its facetings, each face of which is a congruent isosceles triangle. This faceted polyhedron is also a compound — of six irregular triangular pyramids, each of a different color.
The next pair are the standard version, and a faceted version, of the rhombcuboctahedron, also known as the rhombicuboctahedron.
The great rhombcuboctahedron, along with one of its numerous possible facetings, comes next. This polyhedron is also called the great rhombicuboctahedron, as well as the truncated cuboctahedron.
The next pair are the snub cube, one of two Archimedean solids which is chiral, and one of its facetings, which “inherited” its chirality from the original.
The icosidodecahedron, and one of its facetings, are next.
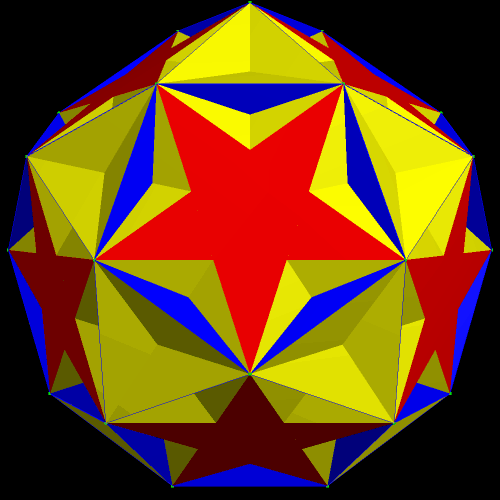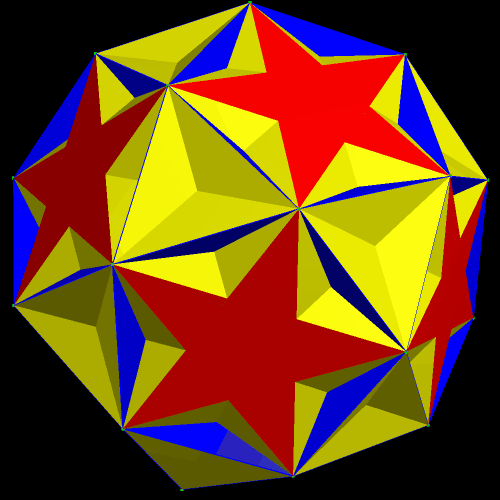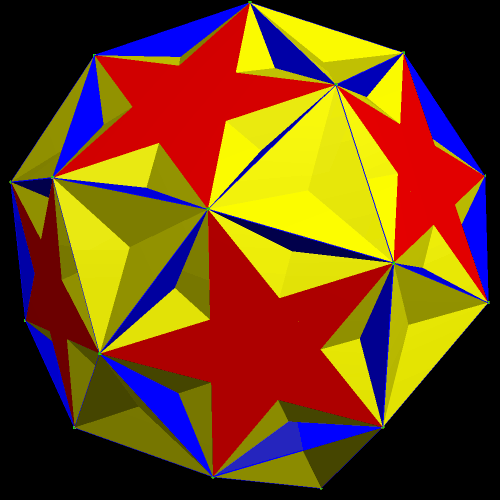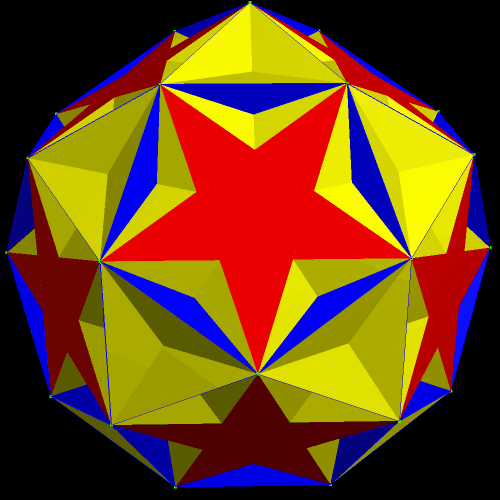
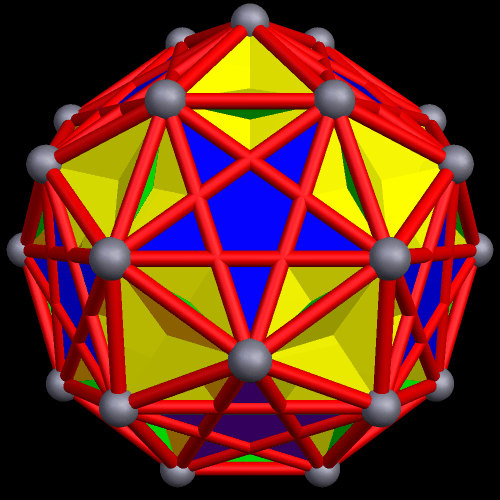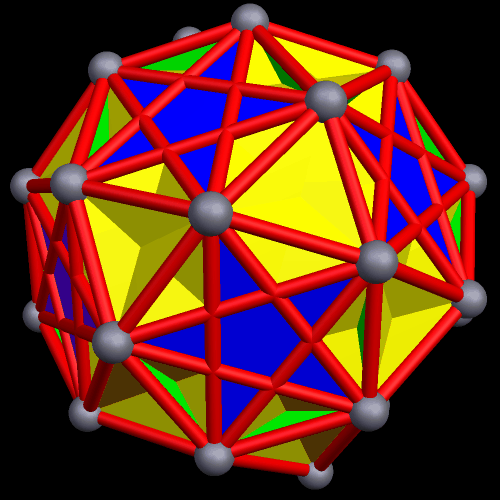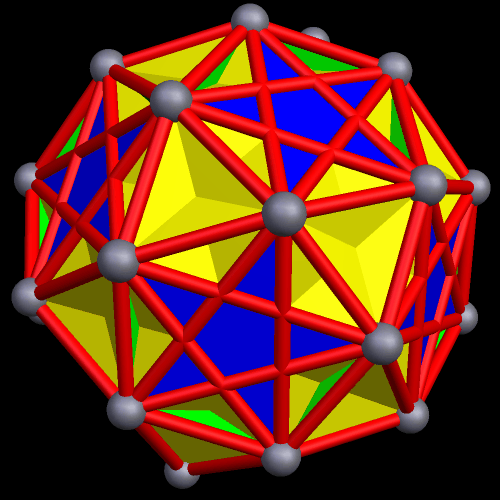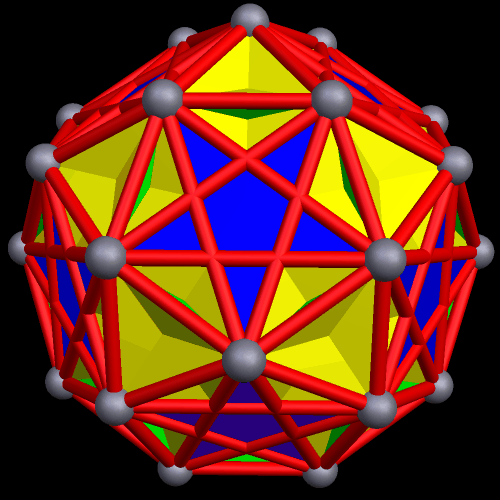
The next pair are the original, and one of the faceted versions, of the rhombicosidodecahedron.
The next two are the great rhombicosidodecahedron, and one of its facetings. This polyhedron is also called the truncated icosidodecahedron.
Finally, here are the snub dodecahedron (the second chiral Archimedean solid, and the only other one, other than the snub cube, which possesses chirality), along with one of the many facetings of that solid. This faceting is also chiral, as are all snub dodecahedron (and snub cube) facetings.
Each of these polyhedral images was created using Stella 4d: Polyhedron Navigator, software available at this website.